
EVERYTHING you need to know about Phishing & Ransomeware.
Share
Both people and Small business owners are at the highest risk of Phishing attacks online. Since they do not have the amenities and safeguards to protect themselves unlike large corporations, they often fall prey to such attacks.
We simplify and break down the different forms of Phishing attacks you might face online and everything you need to know about them. So, take a seat, lay back, turn on some Will Smith 90's hits or whatever you like listening to, and get ready to learn everything you need to know about phishing and ransomware threats, how they work, what they aim for, and how to protect yourself as an individual or small business. Shall we begin?
Why is Phishing Worse Than Ransomware?
Let's start with a classic question, these two best friends are just as bad in my eyes but most people think ransomware is so much worst. Phishing and ransomware are two of the biggest cyber security threats businesses and people face today. Maybe even your place of business has already been hit by them.
Although both types of cyber attacks can be harmful, phishing is actually more dangerous than ransomware since it is the preferred method by cybercriminals for executing ransomware.
Despite their severity and malicious intent, these cyber threats won't go away; however, we'll talk about how you can still protect your data and businesses from these growing threats.
What is Phishing?
Phishing employs simple, genuine-looking emails to get people to give up their personal info. This Information can include login credentials for employee accounts like usernames and passwords, or credit card info. Cybercriminals infect emails with malware when they run phishing attacks.
As individuals and employees find themselves persuaded to click such emails, they are little aware that their inadvertent behavior can result in the loss of sensitive personal data and company data or personal financial loss. For companies, sometimes, the intent of cybercriminals may also be to communicate malicious information against the company in the garb of an authentic entity.
The primary reason phishing is rampant is the inability of individuals to detect phishing attempts. This ensues from a lack of awareness regarding phishing and the latest cyber-attack trends. The prevalent behavior to read an email as soon as it is received in the inbox forces an to focus more on the content and its benefits to one’s own self.
What is Ransomware?
Ransomware is a malware designed to take hostage a computer or mobile device either by locking it or encrypting it. Cybercriminals demand ransom from the victim to unlock or decrypt the device. Malware is a general reference to any code designed to be malicious and take complete control over a computer, network, or mobile device. Ransomware is specific in its operation, which includes locking and taking over access to the victim’s system. The victim gains control over his/ her device or system only after the attackers get their ransom.
Ransomware converts into cyberextortion when cybercriminals remove critical data from the victim’s device and threaten data leakage to get their demands met. Ransomware, in such cases, is referred to as extortionate.
Individuals that fall victim to ransomware face the risk of several damaging losses, including:
- Data loss - Loss of personal information
- Loss of money
- Access limitations
Talking about the corporates and small businesses, Organizations of all sizes are vulnerable to ransomware. Data loss can be deep, including loss of corporate data, crucial employee and financial information, intellectual property data, client data such as patient records, and customer information.
Evolving trends show that ransomware criminals are targeting businesses in sectors such as government, healthcare, education, SMBs, companies with critical infrastructure, and more. These segments are more vulnerable to ransomware attacks. Given the nature of these business sectors, the safest way for them to counter the attacks is to pay up.
Attackers use phishing methods such as spear phishing as their modus operandi to accomplish ransomware attacks successfully.
Ransomware vs Phishing
Cyber attackers prefer phishing and ransomware over other forms of cyber-targeting. There's an important question here: is ransomware more dangerous than phishing?
Phishing is more malicious and cruel than ransomware in many ways because of its inherent structure and the advantages it affords cyber criminals. This is not to say that ransomware may not harm you.
Phishing is the Primary Gateway for Installing Ransomware
Research shows that cybercriminals employ phishing mainly to deliver ransomware. The simplicity of the phishing technique is what makes it more dangerous than ransomware. Attackers find it easy to send a customized email to lure individuals to execute desired actions.
In the corporate world, the lesser an employee’s awareness of phishing, the greater the attacker’s success. Criminals capture employees’ attention and earn their trust using authentic-looking emails.
When employees do as instructed in the email – download an attachment or click a malicious link – ransomware gets embedded in their computer, device, or network. The ransomware then encrypts data, holding the data, and indirectly the victim, hostage till a ransom is paid.
Phishing Facilitates Targeted Methods for High Impact
While phishing basically involves the use of an email, there are several techniques that make it difficult for employees to realize that they are being deceived.
Common Emails
This is one of the most effective and dangerous phishing methods. Employees can be easily misled into believing that the email they received is typical work communication. Some common ways that phishing attackers employ include:
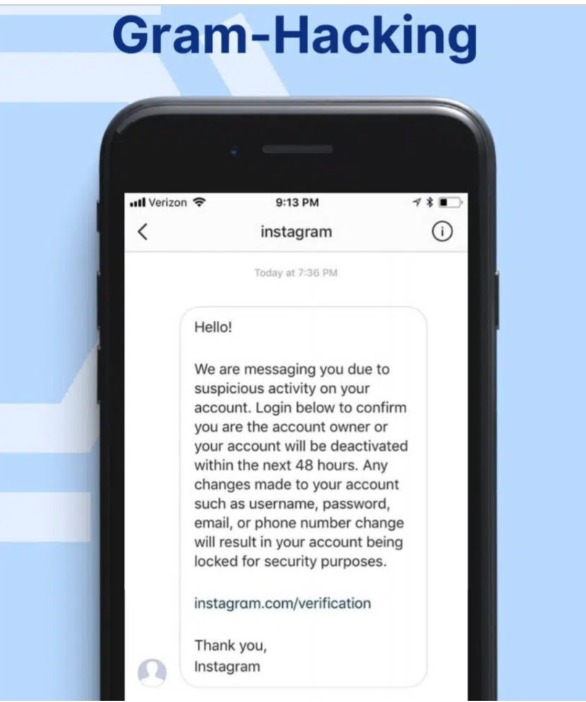
Organizational emails
These phishing emails are similar to company emails employees may receive on a typical workday. Full inbox alert messages, or instructions to download company files from a website or cloud service, are some examples.
Technical Error Notifications
Emails displaying messages such as organizational software error notifications and bounced email reports.
Non-Organizational Business Notifications
Emails with specific commercial information that may or may not be related to your business. Insurance promotion emails are an example.
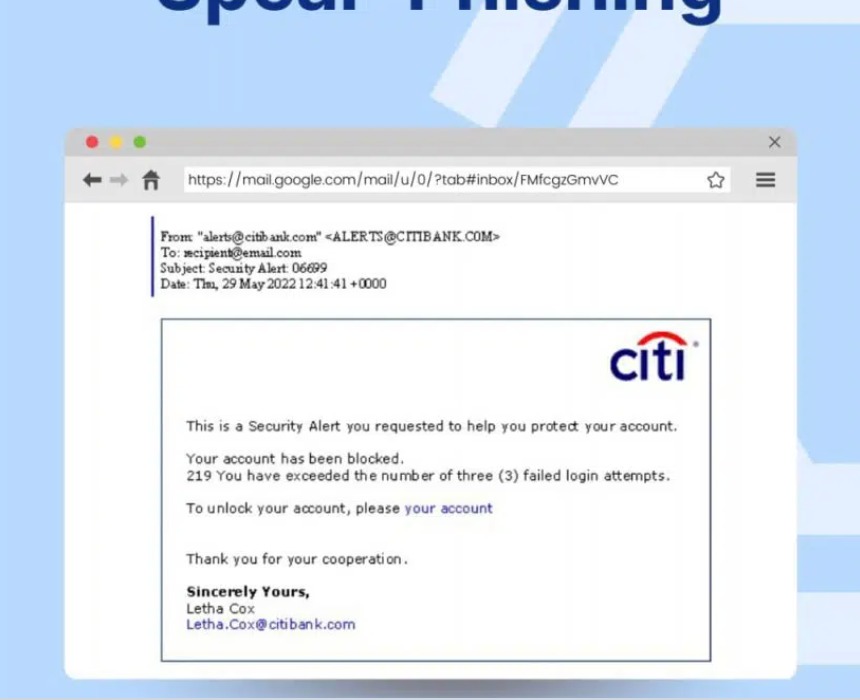
Spear Phishing
Basic security tools like spam protection can't spot this type of phishing. Attackers employing this technique target specific employees, usually those executing key roles, in the organization. Criminals collect information specific to these people and create emails customized to these targeted individuals.
The purpose of these phishing attacks is usually to persuade the employees to give away confidential information. Criminals also use this method to embed malicious malware, including ransomware.
The extremely customized nature of the emails in spear-phishing makes it almost impossible for spam protection and reputation filters to identify the malicious nature of the email.
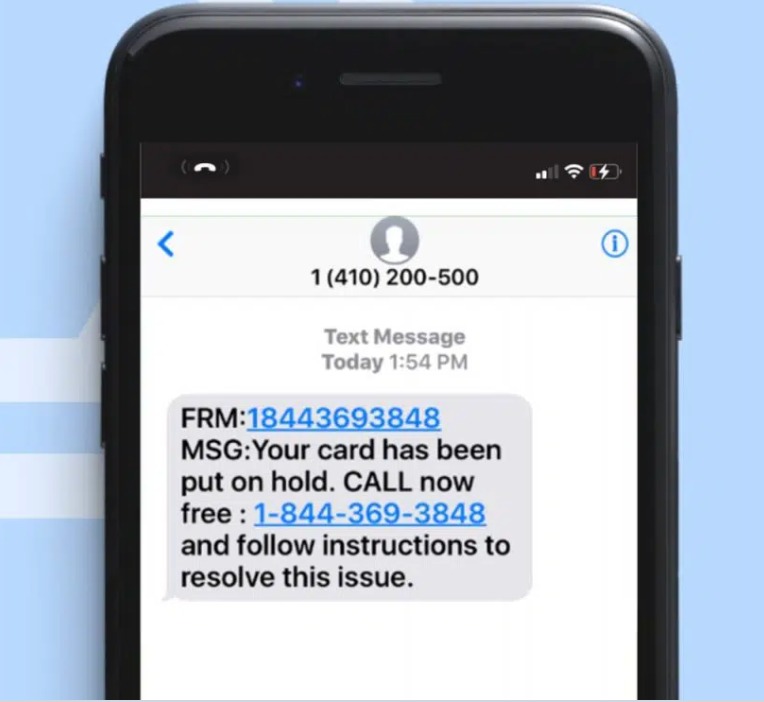
BEC or Business Email Compromise
Attackers create a look-alike of email accounts of executives in highly authoritative positions in your company. Such people may include payroll executives, key people in human resources, and even the company directors and CEO.
Attackers send look-alike emails to employees in decision-making positions in the financial division. In the guise of the company’s top authority, attackers persuade these employees to send to specified accounts. These accounts are obviously under the control of the attackers.
HOW CAN YOU STAY SAFE?
Mobile devices such as smartphones are always working unlike computers, which may be switched off sometimes. This nature of mobile phones makes them the primary target for phishing.
Individuals with mobile devices are more vulnerable to phishing attacks. In a nutshell, basically, we are all at risk! The tendency of users to view and respond to emails as and when they are received increases their vulnerability.
Employees must delay responding to an email through their mobile devices even if the tone of the message sounds urgent. It would be best for employees to verify the email on their computers and then respond if needed. With BYOD – Bring Your Own Devices – culture increasing at workplaces, the need for greater employee awareness regarding data security, app security, and phone security, is greater than ever before.
Mobile security apps such as BodyGuard make life easier for every mobile user. This is a one-button app that secures even the most susceptible IoT devices and mobile phones. The app offers multiple protection against phishing, ransomware, and malware. Yes, it may be hard to digest but it's as simple as that, one App, one button, and your life become instantly more secure! We made sure of that.
As always,
please do keep safe and aware,
Shikha Dutt
Tomer Yair Zemel
And the entire SafeHouse Team 🤙🏿

